Blood
pressure plays a vital role in ensuring a healthy pregnancy. During this
transformative period, the mother’s body undergoes significant physiological
changes, including an increase in blood volume and hormonal shifts. These
changes directly impact cardiovascular health and can lead to fluctuations in
blood pressure. Uncontrolled blood pressure, whether high or low, can result in
conditions like preeclampsia, fetal growth restriction, or preterm delivery.
Proper awareness and proactive measures are key. By understanding how to
maintain stable blood pressure through lifestyle adjustments, regular
monitoring, and timely medical intervention, expectant mothers can reduce risks
and foster a safe, supportive environment for their baby’s development.

Understanding Blood Pressure Changes in Pregnancy
Normal Blood Pressure Ranges for Pregnant Women
During
pregnancy, a woman’s blood pressure often changes due to physiological and
hormonal shifts. A normal blood pressure reading is below 120/80 mmHg. While
slight fluctuations are expected, readings between 120/80 and 140/90 mmHg
should be monitored closely, as they may signal the onset of hypertension.
Blood pressure that consistently exceeds 140/90 mmHg is considered high and can
pose risks for both mother and baby. In contrast, blood pressure below 90/60
mmHg is considered low and may result in symptoms such as dizziness or
fainting. These benchmarks provide a framework for recognizing healthy ranges
and identifying when intervention might be necessary.
Recognizing Symptoms of Hypertension and
Hypotension
Hypertension
during pregnancy often presents with symptoms like severe headaches, vision
disturbances, persistent swelling in the hands or face, and sudden weight gain.
These may indicate preeclampsia, a condition that can lead to serious
complications if untreated. Hypotension, on the other hand, is characterized by
symptoms such as lightheadedness, fatigue, and nausea. It is often caused by
dehydration or lying on the back, which compresses the vena cava and reduces
blood flow to the heart. Recognizing these signs early is essential for taking
timely action, whether through lifestyle adjustments or medical care, to ensure
a healthy pregnancy.
Lifestyle Tips for Managing Blood Pressure
Nutrition Strategies for Healthy Blood Pressure
A
balanced diet is critical for managing blood pressure during pregnancy.
Reducing sodium intake is one of the most effective strategies; avoiding
processed and packaged foods and focusing on fresh produce, whole grains, and
lean proteins can help. Additionally, calcium and magnesium from sources like
yogurt and leafy greens promote vascular health, while omega-3 fatty acids from
fish or supplements can reduce inflammation and support cardiovascular
function. Pregnant women should also be aware of the coffee impact on blood pressure. While moderate caffeine intake is generally
considered safe, excessive consumption can cause temporary spikes in blood
pressure. Limiting coffee and other caffeinated beverages to recommended
levels—about 200 mg of caffeine per day—is advisable.
Safe Physical Activities During Pregnancy
Engaging
in regular physical activity is a cornerstone of managing blood pressure during
pregnancy. Walking is a simple and accessible way to improve circulation and strengthen
the cardiovascular system. Prenatal yoga offers both physical and mental
benefits, enhancing flexibility, reducing stress, and promoting mindfulness.
Swimming is another excellent choice, providing a full-body workout without
placing stress on joints or the spine. Safety should always be the priority.
Avoid high-impact activities, heavy lifting, or exercises that involve lying
flat on the back after the first trimester. Consult with a healthcare provider
to tailor an exercise regimen to individual needs and capabilities.
Monitoring Blood Pressure Safely
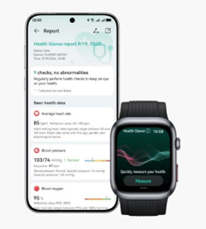
Monitoring
blood pressure regularly is essential for detecting changes early and
addressing them effectively. Modern technology has made this easier, with
devices like the HUAWEI Watch D2 offering dynamic and accurate tracking
tailored to the needs of pregnant women. This smartwatch enables 24/7 blood
pressure monitoring, capturing readings even during sleep to provide a
comprehensive view of daily trends. It also generates weekly blood pressure
reports, giving valuable insights into fluctuations and health patterns. Beyond
blood pressure, the HUAWEI Watch D2 supports comprehensive health management
with features like sleep monitoring, ECG analysis, and pulse rate tracking. Its
advanced sensors collect precise data, making it easier to spot early signs of heart
or vascular issues.
Managing High Blood Pressure Risks
Understanding Preeclampsia and How to Prevent It
Preeclampsia
is a serious condition that affects some pregnant women, characterized by high
blood pressure and signs of organ damage, often to the kidneys or liver. It
typically occurs after the 20th week of pregnancy and can lead to severe
complications if untreated. Risk factors include a history of hypertension,
obesity, or a family history of preeclampsia. Preventive measures focus on
maintaining a healthy lifestyle. A balanced diet low in sodium and rich in
fruits, vegetables, and whole grains is crucial. Regular physical activity,
stress management, and adequate sleep also play significant roles. Prenatal
care is essential for early detection and management.
Medical Interventions and Precautions
For
women with pre-existing hypertension or those who develop it during pregnancy,
medical intervention may be necessary. Antihypertensive medications deemed safe
for pregnancy can help maintain stable blood pressure levels. In some cases,
hospitalization may be required to closely monitor the mother and baby’s
health. Regular prenatal checkups are
critical for identifying complications early. Healthcare providers will often
conduct additional tests, such as urine analysis and ultrasounds, to assess the
baby’s growth and detect signs of stress. Women should also be vigilant about
reporting symptoms like persistent headaches, vision changes, or severe
swelling. Collaborative care between patients and providers ensures that
potential risks are managed effectively, safeguarding maternal and fetal
health.
Conclusion
Managing
blood pressure during pregnancy is a multifaceted endeavor that requires a
combination of lifestyle adjustments, regular monitoring, and medical care.
From understanding normal blood pressure ranges and symptoms of abnormalities
to adopting a nutritious diet, engaging in safe physical activities, and
utilizing modern monitoring tools like the HUAWEI Watch D2, expectant mothers
have numerous resources to support their health. Proactive measures not only
enhance maternal well-being but also create a nurturing environment for the
developing baby. By staying informed and working closely with healthcare
providers, mothers can navigate pregnancy confidently, ensuring the best
possible outcomes for both themselves and their child.
